How To Install Mysql Workbench In Mac
How to Install MySQL 8.0 (on Windows, macOS, Ubuntu) and Get Started with SQL Programming
This article is applicative to MySQL 8.0, which is the successor of MySQL 5.7, where 5 was dropped?!
Introduction to Relational Database and SQL
Relational Databases
A relational database organizes data in tables. A table has rows (or records) and columns (or fields). Tables are related based on common columns to eliminate data redundancy and ensure information integrity.
Popular Relationship Database Management System (RDBMS) includes:
- the commercial Oracle, IBM DB2, Microsoft SQL Server and Access, SAP Hana.
- the open-source MySQL, PostgreSQL, mariaDB, Embedded Apache Derby (Java DB), mSQL (mini-SQL), SQLite, Apache OpenOffice's Base, and mongoDB (non-relational).
Structure Query Linguistic communication (SQL)
A high-level programming language, chosen Structure Query Language (SQL), is designed for interacting with the relational databases. SQL defines a set of commands, such equally SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, CREATE Table, Drop Tabular array, and etc.
Edgar F. Codd of IBM proposed the Relational Database Model in 1970. SQL, one of the earlier programming language, was later on developed by Donald D. Chamberlin and Raymond F. Boyce at IBM in the early on 1970s. Oracle, subsequently, took information technology to a new height.
ANSI (American National Standard Institute) established the showtime SQL standard in 1986 (SQL-86 or SQL-87) - adopted by ISO/IEC as "ISO/IEC 9075" - followed in 1989 (SQL-89), 1992 (SQL-92 or SQL2), 1999 (SQL-99 or SQL3), 2003 (SQL:2003), 2006 (SQL:2006), 2022 (SQL:2011) and 2022 (SQL:2016). Notwithstanding, well-nigh of the database vendors accept their ain directs, e.thousand., PL/SQL (Oracle), Transact-SQL (Microsoft, SAP), PL/pgSQL (PostgreSQL).
SQL By Examples
A relational database arrangement organizes data in the post-obit hierarchy:
- A relational database organisation contains many databases.
- A database comprises tables.
- A table have rows (or records) and columns (or fields).
Suppose nosotros take a database called studentdb, a tabular array called class101 in the database with 3 columns (id, name, gpa) and four rows as illustrated below. Each column has a data type. We choose: INT (integer) for column id, VARCHAR(50) (variable-length string of up to 50 characters) for proper name, and FLOAT (floating-betoken number) for gpa.
Database: studentdb Tabular array: class101 +-----------+--------------------+-------------+ | id (INT) | name (VARCHAR(l)) | gpa (Float) | +-----------+--------------------+-------------+ | 1001 | Tan Ah Teck | 4.v | | 1002 | Mohammed Ali | 4.8 | | 1003 | Kumar | 4.8 | | 1004 | Kevin Jones | iv.6 | +-----------+--------------------+-------------+
SQL (Structure Query Language) defines a set up of intuitive commands (such every bit SELECT, INSERT, DELETE, UPDATE) to interact with relational database system.
SELECT
SELECT column1, column2, ... FROM tableName WHERE criteria SELECT * FROM tableName WHERE criteria SELECT proper noun, gpa FROM class101 +--------------+------+ | proper noun | gpa | +--------------+------+ | Tan Ah Teck | four.5 | | Mohammed Ali | iv.8 | | Kumar | 4.8 | | Kevin Jones | iv.six | +--------------+------+ SELECT * FROM class101 +------+--------------+------+ | id | name | gpa | +------+--------------+------+ | 1001 | Tan Ah Teck | 4.5 | | 1002 | Mohammed Ali | 4.viii | | 1003 | Kumar | 4.8 | | 1004 | Kevin Jones | four.6 | +------+--------------+------+ SELECT name, gpa FROM class101 WHERE gpa >= 4.7 +--------------+------+ | proper name | gpa | +--------------+------+ | Mohammed Ali | 4.eight | | Kumar | 4.8 | +--------------+------+ SELECT proper noun, gpa FROM class101 WHERE proper name = 'Tan Ah Teck' +-------------+------+ | proper name | gpa | +-------------+------+ | Tan Ah Teck | 4.v | +-------------+------+ SELECT name FROM class101 WHERE name Similar 'g%' +-------------+ | name | +-------------+ | Kumar | | Kevin Jones | +-------------+ SELECT * FROM class101 WHERE gpa > 4 AND name Similar 'k%' Gild BY gpa DESC, name ASC +------+-------------+------+ | id | name | gpa | +------+-------------+------+ | 1003 | Kumar | iv.viii | | 1004 | Kevin Jones | 4.6 | +------+-------------+------+
DELETE
DELETE FROM tableName WHERE criteria DELETE FROM class101 DELETE FROM class101 WHERE id = 33 INSERT
INSERT INTO tableName VALUES (firstColumnValue, ..., lastColumnValue) INSERT INTO tableName (column1, column2, ...) VALUES (value1, value2, ...) INSERT INTO class101 VALUES (1001, 'Tan Ah Teck', 4.v) INSERT INTO class101 (name, gpa) VALUES ('Peter Jones', iv.55)
UPDATE
UPDATE tableName Prepare column = value WHERE criteria UPDATE class101 SET gpa = 5.0 UPDATE class101 Ready gpa = gpa + 1.0 WHERE proper noun = 'Tan Ah Teck' CREATE TABLE
CREATE TABLE tableName (column1Name column1Type, column2Name column2Type, ...) CREATE TABLE class101 (id INT, name VARCHAR(50), gpa FLOAT) DROP Table
Driblet TABLE tableName Driblet Table class101 Notes:
- Case Sensitivity: SQL keywords, names (identifiers), strings may or may not be example-sensitive, depending on the implementation.
- In MySQL, the keywords are Non example-sensitive. For clarity, I evidence the keywords in UPPERCASE in this article.
- For programmers, it is BEST to treat the names (identifiers) and strings as case-sensitive.
(In MySQL, column-names are e'er case insensitive; but table-names are example-sensitive in Unix, but instance-insensitive in Windows (dislocated!!). Example-sensitivity in cord comparing depends on the collating sequence used (?!).)
- String: SQL strings are enclosed in unmarried quotes. But about implementations (such as MySQL) accept both single and double quotes.
Introduction to MySQL Relational Database Direction Arrangement (RDBMS)
SQL is a programming language for interacting with relational databases. On the other hand, MySQL is a software - a Relational Database Management Arrangement.
MySQL is ane of the near used, industrial-force, open-source and costless Relational Database Management Organisation (RDBMS). MySQL was developed by Michael "Monty" Widenius and David Axmark in 1995. It was owned by a Swedish visitor chosen MySQL AB, which was bought over past Sun Microsystems in 2008. Sun Microsystems was acquired by Oracle in 2022.
MySQL is successful, not only because it is free and open-source (at that place are many complimentary and open-source databases, such as PostgreSQL, Apache Derby (Java DB), mSQL (mini SQL), SQLite and Apache OpenOffice'due south Base), just also for its speed, ease of use, reliability, performance, connectivity (total networking support), portability (run on well-nigh OSes, such as Unix, Windows, macOS), security (SSL back up), minor size, and rich features. MySQL supports all features expected in a loftier-performance relational database, such as transactions, strange cardinal, replication, subqueries, stored procedures, views and triggers.
MySQL is ofttimes deployed in a LAMP (Linux-Apache-MySQL-PHP), WAMP (Windows-Apache-MySQL-PHP), or MAMP (macOS-Apache-MySQL-PHP) environment. All components in LAMP is free and open-source, inclusive of the Operating Organization.
The mother site for MySQL is https://www.mysql.com. The ultimate reference for MySQL is the "MySQL Reference Transmission", available at https://dev.mysql.com/doc. The reference manual is huge - the PDF has over 3700 pages!!!
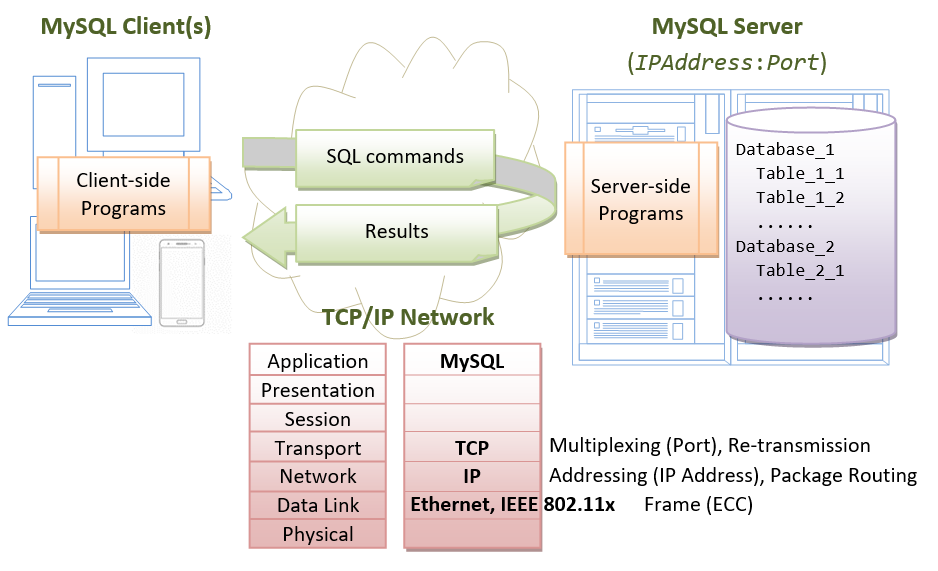
MySQL operates every bit a client-server system over TCP/IP network. The server runs on a motorcar with an IP address on a called TCP port number. The default TCP port number for MySQL is 3306. Users tin admission the server via a client program, connecting to the server at the given IP address and TCP port number.
MariaDB
Extracted from Wiki: MariaDB is a community-developed, commercially supported fork of the MySQL relational database management system (RDBMS), intended to remain free and open up-source software nether the GNU General Public License. Development is led by some of the original developers of MySQL, who forked it due to concerns over its acquisition by Oracle Corporation in 2009.
How to Install MySQL 8.0 and Become Started with SQL Programming
I want y'all to install MySQL on your own machine, because I desire you to learn how to install, customize and operate complex industrial software arrangement. Installation could be the hardest office in this exercise.
Step 0: Create a directory to continue all your works
Of import: Earlier getting started, cheque that you lot take a few GBs of Free Spaces.
Create a directory to keep all your works called:
- (For Windows) "
c:\myWebProject". - (For macOS/Linux) "
~/myWebProject" where "~" denotes your dwelling directory.
c: cd \ mkdir myWebProject cd mkdir myWebProject
Use your graphical interface, e.thou., File Explorer (Windows), or Finder (macOS) to verify this directory. (Of course yous can utilize your graphical interface to create this directory!)
For novices: Information technology is important to follow this step. Otherwise, you will be out-of-sync with this commodity and volition not be able to find your files after.
Step 1: Download and Install MySQL
For Windows
- Download MySQL Community Server "ZIP Archive" from https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/mysql/:
- Under "Full general Availability (GA) Releases" tab.
- Under "MySQL Community Server eight.0.{xx}", where {xx} is the latest update number ⇒ In "Select Operating System", cull "Microsoft Windows".
- Under "Other Downloads", download "Windows (x86, 64-chip), ZIP ARCHIVE (virtually 200MB) (
mysql-viii.0.{twenty}-winx64.nothing)". - Nether "MySQL Community Downloads", in that location is NO need to "Login" or "Sign upwardly" - Just click "No thanks, only offset my downloads!".
- UNZIP the downloaded file into your project directory "
C:\myWebProject". MySQL will be unzipped equally "c:\myWebProject\mysql-8.0.{xx}-winx64". (Right click on the file ⇒ Extract All ⇒ Choose the destination folder as "c:\myWebProject".)
For EASE OF USE, nosotros shall shorten and RENAME the directory to "c:\myWebProject\mysql". Have note and think your MySQL installed directory!!! - (NEW since MySQL 5.7.vii) Initialize the database: Commencement a CMD (as ambassador) ("Search" button ⇒ Enter "cmd" ⇒ Right-Click on "Command Prompt" ⇒ Run as Administrator) and consequence these commands:
c: cd \myWebProject\mysql\bin mysqld --initialize --console ...... ...... [Note] A temporary password is generated for root@localhost: xxxxxxxxDuring the installation, a superuser calledrootis created with a temporary password, every bit shown in a higher place. Take Annotation of the Countersign, COPY and SAVE it somewhere; and TAKE A PICTURE!!!
NOTE: If error "VCRUNTIME140_1.dll was not institute" occurs, check HERE. - If you make a error or forgot your password, DELETE the entire MySQL installed directory "
C:\myWebProject\mysql", and Echo step 2 and iii.
For macOS
Notes: The latest version of MySQL (8.0.28) works with macOS Large Slur (11) and Monterey (12). If you are running older version of macOS, you lot may demand to detect an archived version of MySQL @ https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/ ⇒ Archive.
- Download the MySQL Community Server "DMG Archive" from https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/mysql/:
- Nether "General Availability (GA) Releases" tab.
- Under "MySQL Community Server 8.0.{xx}", where {xx} is the latest update number ⇒ In "Select Operating System", choose the "macOS".
- Select the advisable "macOS 11 (x86, 64-flake) DMG Annal" for macOS 11 or 12 (
mysql-eight.0.{xx}-macos11-x86_64.dmg) (If your mac is running on the ARM processor (Apple M1), then cull the "macOS11 (ARM, 64-scrap) DMG Archive").- To check your OS version ⇒ Click the 'Apple' logo ⇒ "Nearly this Mac".
- To check your processor ⇒ Click the 'Apple tree' logo ⇒ look for "Intel" (x86); or "Apple M1" (ARM processor).
- To check whether your macOS is 32-fleck or 64-bit ⇒ Read http://back up.apple.com/kb/ht3696. Unless you lot have a dinosaur-era motorcar, information technology should be 64-bit!
- There is NO need to "Login" or "Sign upwards" - Just click "No thanks, simply commencement my download".
- To install MySQL (Run into https://dev.mysql.com/physician/refman/eight.0/en/osx-installation-pkg.html for screen shots):
- Go to "Downloads" ⇒ Double-click "
.dmg" file downloaded. - Double-click the "
.pkg". - In "Introduction", click "Continue".
- In "License", choose "Agree".
- In "Installation Type", click "Install".
- In "Configuration", choose "Use Strong Countersign Encryption", and enter a password for the "root" user. Brand sure you remember your countersign.
- MySQL will be installed in "
/usr/local/mysql". Have note of this installed directory!! - Eject the ".
dmg" file.
- Go to "Downloads" ⇒ Double-click "
- If you make a fault or forgot your countersign, terminate the server (Click "Apple" Icon ⇒ System Preferences ⇒ MySQL ⇒ Stop).
Goto/usr/local(via Finder ⇒ Become ⇒ GoTo Binder ⇒ blazon/usr/local) and remove all the folders beginning with "mysql...", due east.g., "mysql-eight.0.{xx}..." and "mysql", and Re-run Step 2.
I shall presume that MySQL is installed in directory "c:\myWebProject\mysql" (for Windows) or "/usr/local/mysql" (for macOS). But you need to TAKE NOTE OF YOUR MySQL INSTALLED DIRECTORY . Hereafter, I shall denote the MySQL installed directory as <MYSQL_HOME> in this article.
Footstep three: Offset the "Server"
The MySQL is a client-server system. The database is run as a server application. Users access the database server via a client program, locally or remotely thru the network, equally illustrated:
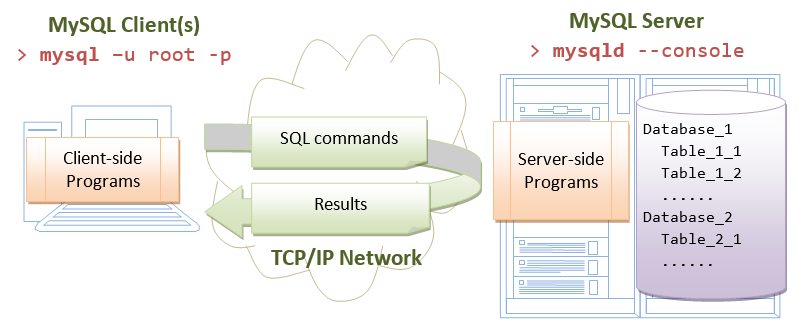
- The server program is chosen "
mysqld" (with a suffix'd', which stands for daemon - a daemon is a non-interactive procedure running in the groundwork). - The customer plan is chosen "
mysql" (without the'd').
The programs mysqld and mysql are kept in the "bin" sub-directory of the MySQL installed directory.
Startup Server
For Windows
To offset the database server, launch a new CMD beat out:
c: cd \myWebProject\mysql\bin mysqld --console ...... ...... XXXXXX Twenty:Xx:XX [Note] mysqld: ready for connections. Version: '8.0.twenty' socket: '' port: 3306 MySQL Customs Server (GPL)
Notation: The --panel option directs the output letters to the console. Without this pick, y'all will see a blank screen.
For macOS
The Easy WAY: Via graphical control. Click "Apple" Icon ⇒ System Preferences ⇒ MySQL ⇒ Start or Finish.
The MySQL database server is now started, and ready to handle clients' requests.
Anything that can peradventure become wrong, does! Read "How to Debug".
Shutdown Server
For Windows
The quickest way to close down the database server is to press Ctrl-C to initiate a normal shutdown. Exercise NOT Kill the server via the window's Shut button.
Observe these messages from the MySQL server console:
XXXXXX XX:20:XX [Notation] mysqld: Normal shutdown ...... XXXXXX XX:XX:Xx InnoDB: Starting shutdown... XXXXXX Twenty:20:20 InnoDB: Shutdown completed; log sequence number 0 44233 ...... XXXXXX XX:XX:Xx [Note] mysqld: Shutdown consummate (You may need to press ENTER to get the command prompt?!)
For macOS
The EASY WAY: Via the graphical control. Click "Apple tree" Icon ⇒ Organisation Preferences ⇒ MySQL ⇒ Stop.
WARNING: You lot should properly shutdown the MySQL server. Otherwise, you might corrupt the database and might take bug restarting it. BUT, if you run into problem shutting downwards the server normally, yous may kill the "mysqld" process in Chore Director (for Windows); or Activity Monitor (for macOS); or System Monitor (for Ubuntu).
Footstep iv: Start a "Customer"
Recall that the MySQL is a customer-server arrangement. One time the server is started, ane or more clients can be connected to the database server. A client could be run on the same automobile (local client); or from another automobile over the network (remote client).
To login to the MySQL server, you need to provide a username and password. During the installation, MySQL creates a superuser chosen "root" with a temporary countersign. I promise that yous have taken note of this password! (Otherwise, re-install!)
The MySQL installation provides a command-line client program called "mysql". (Recall that the server plan is called "mysqld" with a suffix 'd'; the client programme does non accept the suffix 'd').
Let's kickoff a command-line client with the superuser "root".
First, make sure that the server is running. See previous stride to re-offset the server if information technology has been shutdown.
For Windows
Start Another NEW CMD vanquish to run the client (You need to continue the CMD that run the server):
c: cd \myWebProject\mysql\bin mysql -u root -p Enter password: // Enter the root's password set during installation. Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MySQL connexion id is one Server version: 8.0.xx Type 'help;' or '\h' for assistance. Type '\c' to articulate the current input statement. mysql>
For macOS
Open a NEW "Last" and issue these commands to first a MySQL customer with superuser root:
cd /usr/local/mysql/bin ./mysql -u root -p Enter countersign: // Enter the root's password given during installation. You will NOT any * for maximum security Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \yard. ...... mysql>
(Skip Unless...) Read "How to Debug".
Step five: Change the Countersign for the Superuser "root"
As mentioned earlier, the MySQL installation creates a superuser chosen "root" with a temporary random countersign. "root" is a privileged user that tin do anything, including deleting all the databases. You are required to change the root's countersign immediately after logging in.
Notes: If y'all go stuck entering a command, press Ctrl-C to abort the current command.
Changing the Password for "root"
Let'southward continue with our client session started before.
mysql> alter user 'root'@'localhost' identified by 'xxxx'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> select Host, User, authentication_string from mysql.user; +-----------+------------------+---------------------------+ | Host | User | authentication_string | +-----------+------------------+---------------------------+ | localhost | root | $A$005.... | | .... | .... | ........ | +-----------+------------------+---------------------------+ mysql> quit Goodbye Re-Get-go a Client as "root" with the New Password
Nosotros have just changed the password for root and exited the client. Start a client and login as root again. Enter the password when prompted.
For Windows
c: cd \myWebProject\mysql\bin mysql -u root -p Enter countersign: Welcome to the MySQL monitor. ...... mysql> For macOS
cd /usr/local/mysql/bin ./mysql -u root -p Enter password: Welcome to the MySQL monitor. ...... mysql> Step half-dozen: Create a New User
The superuser "root" is privileged, which is meant for database assistants and is not meant for operational. We shall create a new user - let'south phone call information technology "myuser" - with a lesser privilege. To create a new user, start a client with superuser "root":
mysql -u root -p ./mysql -u root -p mysql> create user 'myuser'@'localhost' identified by 'xxxx'; Query OK (0.01 sec) mysql> grant all on *.* to 'myuser'@'localhost'; Query OK (0.01 sec) mysql> quit Caption
- CREATE USER 'myuser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED By 'xxxx'
Nosotros use the command "create user" to create a new user chosen'myuser'@'localhost', who can login to the server locally from the same motorcar (but non remotely from some other machine), with password "xxxx". - GRANT ALL ON *.* TO 'myuser'@'localhost'
The newly created user has NO privilege to perform any database operation includingselect. We use the "grant" command to grant "all" the privileges (includingselect,insert,delete, and and then on) to this new user on ALL the databases and ALL the tables ("on *.*"). This new user, in exercise, has the same privilege asroot, except that it cannot issuegrantcommand. For production, you lot should grant only the necessary privileges on selected databases and selected tables, due east.g., "grant select,insert,update on studentdb.*" - it tin can effectselect,insertandupdate(but nodelete,create/drop table) on ALL the tables of the databasestudentdbonly.
Step 7: Create a new Database, a new Table in the Database, Insert Records, Query and Update
Recall that the MySQL server organizes data in the following hierarchy:
- A system contains many databases.
- A database contains many tables.
- A table contains rows (records) and columns (fields).
Let's create a database called "studentdb", and a table called "class101" in the database. The table shall take three columns: id (of the blazon INT - integer), name (of the type VARCHAR(l) - variable-length string of up to 50 characters), gpa (of the type FLOAT - floating-indicate number).
Circumspection: Programmers don't apply blank and special characters in NAMES (database names, table names, column names). It is either non supported, or will pose y'all many more than challenges.
Tips on Client's Session (Come Back to this Section If Yous Get Stuck in Running Control)
Before we go along, here are some tips on using the client:
- Y'all need to terminate your command with a semicolon (
;), which sends the command to the server for processing. East.grand.,mysql> select * from class101; - A command tin can span several lines. The prompt for subsequent lines changes to
->to denote continuation. You need to terminate the command with a semicolon (;). E.g.,mysql> select * -> from class101 -> -> ;In other words, if y'all forget to type';', y'all can type the';'on the next line. - Y'all can use
\cto cancel (abort) the current command. E.k.,mysql> select * from class101 \c - If you open a single/double quote, without closing it, the continuation prompt changes to
'>or">(instead of->). For instance,mysql> select 'xxx '> ' -> \c mysql> select "xxx "> " -> \c
- You tin can too press Ctrl-C to arrest the electric current command.
- You can use up/downward arrow keys to remember the previous/adjacent commands, from the "command history".
- (For Windows x) You should enable Copy/Paste functions of CMD shell. To enable Copy/Paste, click the CMD'southward icon ⇒ Properties ⇒ Options ⇒ Edit Options ⇒ Check "Enable Ctrl key shortcuts". You can then utilise Ctrl-C/Ctrl-V for Copy/Paste.
SQL Programming
Let'south start a client with our newly-created user "myuser".
mysql -u myuser -p ./mysql -u myuser -p mysql> create database if non exists studentdb; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.08 sec) mysql> show databases; +--------------------+ | Database | +--------------------+ | ...... | | studentdb | | ...... | +--------------------+ ten rows in set up (0.07 sec) mysql> employ studentdb; Database changed mysql> drop table if exists class101; Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.xv sec) mysql> create tabular array class101 (id int, name varchar(50), gpa bladder); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.15 sec) mysql> bear witness tables; +---------------------+ | Tables_in_studentdb | +---------------------+ | class101 | +---------------------+ ane row in fix (0.00 sec) mysql> depict class101; +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Blazon | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | id | int(11) | Yep | | Aught | | | name | varchar(50) | Yeah | | Cipher | | | gpa | float | YES | | Cypher | | +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ three rows in set (0.04 sec) mysql> insert into class101 values (eleven, 'Tan Ah Teck', four.viii); Query OK, i row affected (0.03 sec) mysql> insert into class101 values (22, 'Mohamed Ali', 4.nine); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.03 sec) mysql> select * from class101; +----+-------------+------+ | id | proper noun | gpa | +----+-------------+------+ | 11 | Tan Ah Teck | four.8 | | 22 | Mohamed Ali | 4.9 | +----+-------------+------+ two rows in set up (0.00 sec) mysql> select name, gpa from class101 where gpa > iv.85; +-------------+------+ | name | gpa | +-------------+------+ | Mohamed Ali | 4.9 | +-------------+------+ 1 rows in set up (0.00 sec) mysql> update class101 set gpa = iv.four where name = 'Tan Ah Teck'; Query OK, ane row affected (0.05 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Inverse: ane Warnings: 0 mysql> select * from class101; +----+-------------+------+ | id | proper noun | gpa | +----+-------------+------+ | 11 | Tan Ah Teck | 4.iv | | 22 | Mohamed Ali | 4.nine | +----+-------------+------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> delete from class101 where id = 22; Query OK, 1 row afflicted (0.03 sec) mysql> select * from class101; +----+-------------+------+ | id | proper noun | gpa | +----+-------------+------+ | 11 | Tan Ah Teck | four.4 | +----+-------------+------+ i rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> source c:\myWebProject\mycommands.sql mysql> source ~/myWebProject/mycommands.sql Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) Query OK, 1 row afflicted (0.00 sec) +------+-------------+------+ | id | name | gpa | +------+-------------+------+ | 11 | Tan Ah Teck | four.4 | | 33 | Kumar | 4.viii | | 44 | Kevin | 4.vi | +------+-------------+------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
Exercises:
- Select records with names starting with letter
'K'. (Hints:proper name like 'Chiliad%', come across Section "SQL by Examples") - Select records with names NOT starting with alphabetic character
'K'. (Hints:proper name Not similar ...) - Select records with
gpabetween 4.35 and 4.65. (Hints:exam-1 AND test-2) - Select records with names having a letter
'eastward'. (Hints:proper name like '%e%') - Select records with names having a letter
'e'or'a'. (Hints:test-ane OR test-2) - Select records with names having a alphabetic character
'e'andgpa ≥ 4.v.
(Skip Unless... ) Read "How to Debug".
More Exercises
- Testify all the databases.
- Create a new database called "
ABCTrading". - Set the "
ABCTrading" database as the default database. - Show all the tables in the default database.
- Create a new table called "
products" with the columns and type indicated below.+-------+----------+-------------+----------+---------+ | id | category | name | quantity | toll | | (INT) | CHAR(iii) | VARCHAR(20) | (INT) | (FLOAT) | +-------+----------+-------------+----------+---------+ | 1001 | PEN | Pen Red | 5000 | one.23 | | 1002 | PEN | Pen Bluish | 8000 | ane.25 | | 1003 | PEN | Pen Black | 2000 | 1.25 | | 1004 | PCL | Pencil 2B | 10000 | 0.49 | | 1005 | PCL | Pencil 2H | 9000 | 0.48 | +-------+----------+-------------+----------+---------+
- Show the table description.
- Insert the above records and list all the records.
- List records with name containing "
Pencil". - Listing records with price ≥ i.0.
- Increase the price of all items by 10%, and list all the records.
- Remove "Pen Ruby" from the table, and listing all the records.
Many-to-many Human relationship
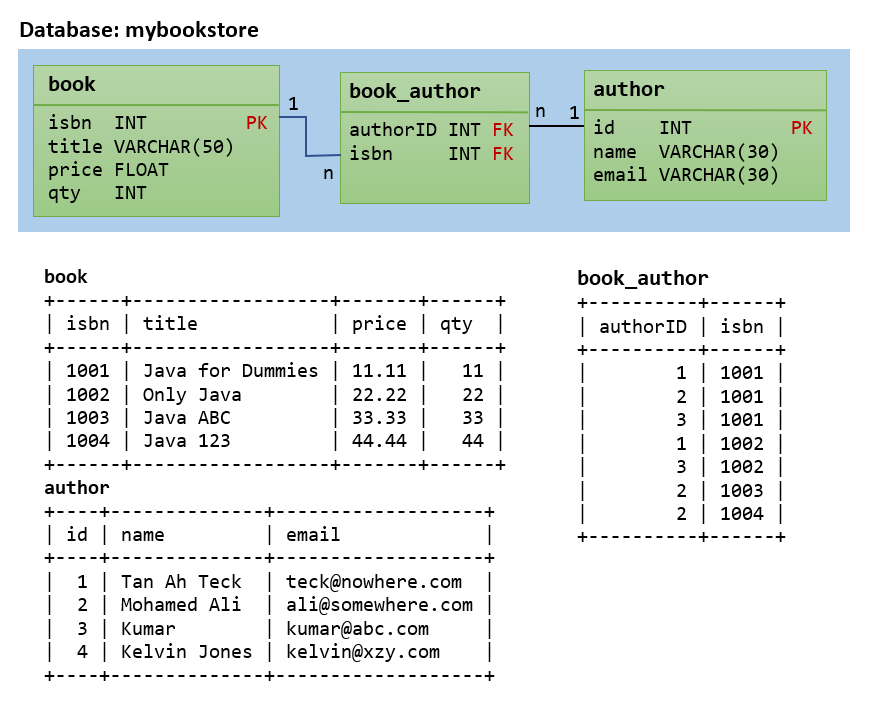
In a bookstore, a book is written past ane or more than authors; an author may write aught or more books. This is known as a many-to-many relationship. Information technology is Incommunicable to capture many-to-many human relationship in a Unmarried table (or one spreadsheet) with a fixed number of columns, without duplicating any piece of data! For example, if you organize the data in the tabular array below, you will not know how many writer columns to be used; and you need to repeat all the data for repeating authors.

The many-to-many relationship between books and authors can be modeled with iii tables, equally shown below. A books table contains data most books (such as title and cost); an authors table contains data most the authors (such every bit proper name and electronic mail). A table chosen books_authors joins the books and authors tables and captures the many-to-many relationship between books and authors.
Exercises
- Create a database called "
mybookstore". - Apply "
mybookstore" as the default database. - Create three tables "
books", "authors", and "books_authors" in the database "mybookstore", with column names and types every bit shown in the database diagram. - Insert the respective records into the tables, and list the contents of each of the tables.
- Try this query and explicate the output:
SELECT books.title, books.price, authors.proper noun FROM books, books_authors, authors WHERE books.isbn = books_authors.isbn AND authors.authorID = books_authors.authorID AND authors.proper name = 'Tan Ah Teck';
- Try this query and discover how the tables are joined:
SELECT books.title, books.price, authors.name FROM books, books_authors, authors WHERE books.isbn = books_authors.isbn AND authors.authorID = books_authors.authorID ;
- Listing all the books (
title,price,qty) by "Tan Ah Teck" withcostless than20. - List all the authors (
proper nameandemail) for the book title "Java for Dummies". - List all the books (
title,price,qty) and all the authors (nameande-mail) for books with title first with "Coffee" (Hints:championship LIKE 'Java%').
(Optional) Backup and Restore Databases
Fill-in via "mysqldump" Utility Program
You can use the "mysqldump" utility program to back up (i) the entire server (all databases), (2) selected databases, or (2) selected tables of a database. The "mysqldump" program generates a SQL script that can later exist executed to copy the databases, tables and their rows.
For example, the post-obit command backups the entire "studentdb" database to a SQL script chosen "backup_studentdb.sql".
For Windows
c: cd \myWebProject\mysql\bin mysqldump -u myuser -p --databases studentdb > "c:\myWebProject\backup_studentdb.sql"
For macOS
cd /usr/local/mysql/bin ./mysqldump -u myuser -p --databases studentdb > ~/myWebProject/backup_studentdb.sql
Study the output file, which contains CREATE DATABASE, CREATE TABLE and INSERT statements to re-create the database and tables dumped earlier.
Restore via "source" command in a mysql client
You tin restore from the fill-in by running the "source" command in a MySQL client. For example, to restore the studentdb fill-in earlier:
For Windows
c: cd \myWebProject\mysql\bin mysql -u myuser -p mysql> driblet database if exists studentdb; mysql> source c:\myWebProject\backup_studentdb.sql
For macOS
cd /usr/local/mysql/bin ./mysql -u myuser -p mysql> drop database if exists studentdb; mysql> source ~/myWebProject/backup_studentdb.sql
Summary of Frequently-Used Commands
(For Windows) Starting MySQL Server and Client
cd path-to-mysql-bin mysqld --panel Ctrl-c cd path-to-mysql-bin mysql -u username -p
(For macOS) Starting MySQL Server and Client
cd /usr/local/mysql/bin ./mysql -u username -p
Oftentimes-used MySQL Commands
MySQL commands are Non case sensitive.
; \c DROP DATABASE databaseName; Driblet DATABASE IF EXISTS databaseName; CREATE DATABASE databaseName; CREATE DATABASE IF Non EXISTS databaseName; Show DATABASES; USE databaseName Drop TABLE tableName; DROP Tabular array IF EXISTS tableName; CREATE TABLE tableName (column1Definition, column2Definition, ...); CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS tableName (column1Definition, column2Definition, ...); Bear witness TABLES; DESCRIBE tableName; DESC tableName; INSERT INTO tableName VALUES (column1Value, column2Value,...); INSERT INTO tableName (column1Name, ..., columnNName) VALUES (column1Value, ..., columnNValue); DELETE FROM tableName WHERE criteria; UPDATE tableName SET columnName = expression WHERE criteria; SELECT column1Name, column2Name, ... FROM tableName WHERE criteria ORDER BY columnAName ASC|DESC, columnBName ASC|DESC, ...; SOURCE full-Path-Filename
(Skip Unless...) How to Debug?
"Everything that can possibly go wrong will get wrong." The virtually important thing to practice is to find the ERROR MESSAGES !!!
"VCRUNTIME140_1.dll was non found" when Running the Initialization for Windows
CAUSE: You lot do non have the required "Microsoft Visual C++ redistributable runtime".
SOLUTION: Goto "The latest supported Visual C++ downloads" @ https://support.microsoft.com/en-gb/aid/2977003/the-latest-supported-visual-c-downloads ⇒ Download "x64: vc_redist.x64.exe" ⇒ run the executable to install "Microsoft Visual C++ 2022-2019 redistributable (x64)" ⇒ Restart your computer ⇒ Yous can observe "vcruntime140_1.dll" nether "C:\Windows\System32".
Cannot Start the MySQL Server afterward Installation
Kickoff of all, check if you take already started an instance of MySQL Server:
- For Windows, beginning the "Task Manager", select "Processes" and look for "
mysqld" processes. "End" all the "mysqld" processes. - For macOS, start the "Activeness Monitor", select "All Processes" and await for "
mysqld" processes. "Kill" all the "mysqld" processes. - For Ubuntu, start the "System Monitor" and await for "
mysqld" processes. "Impale" all the "mysqld" processes.
SYMPTOM: Cannot outset mysql server Error Letters: xxxxxx [InnoDB] The innodb_system data file 'ibdata1' must exist writable xxxxxx [InnoDB] The innodb_system data file 'ibdata1' must be writable xxxxxx [Server] Failed to initialize DD Storage Engine xxxxxx [Server] Information Dictionary initialization failed. xxxxxx [Server] Aborting Likely CAUSES: A MySQL server has already started holding on to the databases POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS: Shutdown or Kill the current server, before starting a new ane. "Permission Denied" in creating temp files under macOS
No more deejay space?!
Cannot Start the "mysql" Client
SYMPTOM: Cannot start mysql client ERROR Message: error 2003 (HY000): Can't connect to MySQL server on 'localhost' (10061) Probable CAUSES: ane. MySQL Server is NOT started, or 2. The client was connecting to the incorrect port number POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS: 1. Bank check to make sure that the MySQL server has been started. Annotation downwards the server's port number from the server's console. 2. Run a client with command "mysql -u root --port=xxxx" to specify the server's port number manually. three. Check "my.ini", make sure that you have a [client] section with port=xxxx. SYMPTOM: Cannot start mysql customer ERROR MESSAGE: fault 2005 (hy000) unknown mysql server host 'localhost' PROBABLE CAUSES: Somehow your localhost is not bound to 127.0.0.1 POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS: 1. Try "ping localhost" to check if "localhost" exists. 2. (Windows) Check "C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts" file. There should be an entry: 127.0.0.1 localhost Remove all the other localhost entries, if any.
Mistake Using the "mysql" Client
Error MESSAGE: Stuck at inbound SQL commands Likely CAUSES: Syntax errors in the current control POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS: 1) Abort the electric current control pressing Ctrl-C two) Arrest the current control using \c a) Enter \c if the prompt is -> or mysql> b) Enter '\c if the prompt is '> c) Enter "\c if the prompt is "> Fault Bulletin: mistake 1046 (3D000): No database selected PROBABLE CAUSES: The default database is not set POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS: 1) Consequence command "use database" to set the default database, or 2) Use the fully-qualified name in the form of "databaseName.tableName". Error MESSAGE: fault 1005 (HY000): Can't create tabular array '...' (errno: 150) PROBABLE CAUSES: A foreign fundamental references a parent table's column which is not indexed. Create index for that column in the parent tabular array. ERROR MESSAGE: ERROR 1396 (HY000): Performance CREATE USER failed for 'myuser'@'localhost' PROBABLE CAUSES: This user already created! SYMPTOM: Logical error in comparison floating betoken numbers for equality. For example, "SELECT * FROM class101 WHERE gpa = 4.4" yields empty fix although there is a tape with gpa=4.4. PROBABLE CAUSES: "gpa" has the blazon of Float. Floating point numbers are not stored "accurately". POSSIBLE SOLUTION: Exercise not compare 2 floating point number for equality. Instead, specify a range, due east.g., "gpa > 3.9 AND gpa < four.1"
Link to MySQL References & Resources
Latest version tested: MySQL Community Server eight.0.28, Windows x, macOS 11, Ubuntu 18.04LTS
Last modified: Feb, 2022
Source: https://www3.ntu.edu.sg/home/ehchua/programming/sql/MySQL_HowTo.html
Posted by: hansleyplithere1970.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Install Mysql Workbench In Mac"
Post a Comment